——A Study of the Innovative Model University-Government-Industry Econet
MA Yongbin
(SchoolofContinuing Education,TsinghuaUniversity)
Abstract: The key to building a national innovation system lies in the construction of an effective university-government-industry cooperation model. University- government- industry Econet has formed an effective cooperative innovation system, changed the traditional knowledge innovation models by splitting the various links of innovation into different universities, government and enterprises. It takes advantage of the specialized production or service of its specific members to fully develop the competitive advantage in specific links and improves the efficiency of innovation through cooperation among its members. Based on the above analysis, University-Government-Industry Econet has provided a new perspective to the construction of national innovation system.
Keywords: econe, innovation system, role, functional analysis
Since the end of 1980s, the cooperative relationship between universities, governments and industry has become center of attention, which triggered related works in academic area. In 1995, the research regarded to this field finally took form, symbolized by the concept American researcher Dr. Henry Etzkowitz and Dr. Leydesdorff fromHollandproposed—the “Triple Helix” model for University-Industry-Government innovation. Triple Helix indicates that, as the core institute of the society, universities, government and corporations should cooperate and coordinate to give full play of their capabilities while keep their own identity. In their cooperation, each institute can either play their own part or become the group leader for innovation.[1] This pattern enjoyed academic recognition across the world, and became the main stream dominating research on the tri-party relationship.
Based on the research result from the past, this paper presents a more efficient resource allocating pattern: University- Government-Industry Econet. As the subject of the Econet, universities, governments, and industry play different roles in the innovation within the net. Their co-influence promotes innovation in the Econet, and establishes the innovation system.
1.Econet
From 1990s, under the influence of knowledge economy and the building of national innovative system, universities, governments, and corporations have been bound together by common interest demands. Since then, a cross-organizational relationship is forming, within which the three parties influence and depend on each other. In practice, universities share some corporative functions; corporations developed new technology with universities and recruit talents from universities; the governments assist universities and corporations to build technology development center, encouraging research on Sci-tech. Therefore, we develop the “triple helix” pattern into an Econet pattern. Econet means a sum up of stable, innovation-oriented, locally-rooted official and non-official relations built in the process of influence and cooperation between universities, governments and industry.
Different from “triple helix,” common growth is the new target for Econet. Through cooperation and competition, interdependent sub-systems grow both independently and commonly, while adjust itself, which constructs new systems. These new systems are the results of common growth of every participants, and push the growth of the whole Econet. The three parties form a value chain, and the interactions between different chains form a value net, through which substance, energy and information trade and flow among participants. Nevertheless, the relationship among participants does not follow the “eat-eaten” pattern of food chain in the natural world, but the exchange of value and interest, for the purpose of a win-win situation. Therefore, the two sides of a link on the value chain co-exist together, and several co-exited sides weave a value net. Pic.1 shows the structure and interaction of the Econet.
As the picture shows, the three parties and the external environment are bound to each other, shaping the pattern of Econet. In this net, the three parties are the “nodes”; the lines are the connections between them, indicating the flow of resources like information, talents, capital, and policy. The communication among the parties can be formal, like trade, exhibition, business talk and seminars, as well as informal. Also, Econet provides a much wider platform than hierarchical organizations for multi-dimensional innovation. Thus, Econet surpasses hierarchical organization in flexibility, and exceeded market-oriented organization in stability.
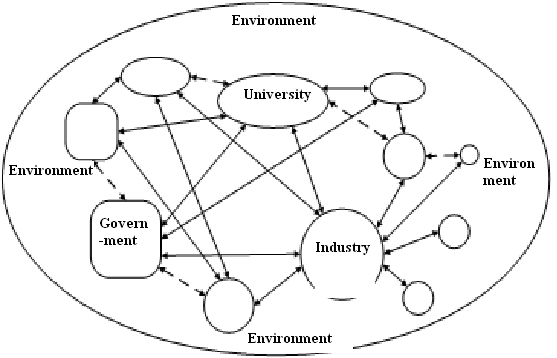
Pic.1 Structure of University-Government-Industry Econet
2.Innovative Mechanism of the Econet
The priority of the Econet, innovation, is motivated by the interaction and resource sharing. Incented by the win-win situation brought by resource sharing, the three parties are tightly bounded, to gain synergistic innovation. By collaborating with industries, universities can put their research result into productivity. In this way, they will gain economic benefits to support research and school running to train people fit to the development of economy and society. Also, industry may be benefited from universities on human resources and technology needed for innovation, while boost the employment rate. Moreover, through building an innovative system encouraging the cooperation among universities, research institutes and industry, the government should create an ideal atmosphere to allocate resources for innovation, and finally ensures a healthy development of the Econet. As can be seen, the most critical goal for University-Industry-Government Econet is to upgrade the innovative capability through the interaction, cooperation and communication among all parties concerned.
An innovative activity has four stages: the emergence of demand on innovation, developing innovative technology, transformation of innovative technology, and the massive production of the fruit of innovation. These four stages form a continuous and closed innovative chain, in which the three parties play different roles while influence each other. These influences propel the development of innovation, and thus the University- Industry- Government innovation system is built.
On the first stage, the university is the receiver of information on innovation accepting the potential demand from the government and industry. Policy guidance from the industry plan of the government, and the direction that the corporations choose to meet the demand from the market, co-decide the content and direction of the demand on innovation.
Under the incentive of demand, the innovation steps into the second stage: the research and development of technology, completed in laboratory. This time, university becomes the subject of innovation. With the knowledge and talents, universities are able to bring about new technology. At this stage, the government and industry are supporting parties: the government builds the environment and support financially through implementing policies, while the industry will also finance the research programs in college and provide personnel resource.
After research and development stage, technology will inevitably step into the transformation stage when corporation becomes the subject of innovation. The corporations possess high sensitivity over the market, so when they join hands with universities, the application research will take place, which will guarantee the mass production of the technology. The government supports innovation with policy and finance.
Next stage is the commercialization of technology, since only market can judge the effectiveness of innovation. Based on the feedback from the market, the new technology can be upgraded as new demands emerging, which takes technology into the next cycle. Since university plays the role of giving birth to new hi-tech corporations, commercialization is a stage that new businesses must go through to survive the market. As the effect of this stage relies on government’s regulation over the market, policies should be implemented to build a healthy market, the most critical of which should be the intellectual property protection system.
Therefore, the innovation mechanism of Econet is to distribute each stage of innovation to different universities, governments and industry. So each member in the network can apply their advantage on the stage that they are specialized in, and promote efficient innovation through their collaboration, as shown in Pic.2. Each contributing factor is implanted in the network, to cultivate a better result as a whole.
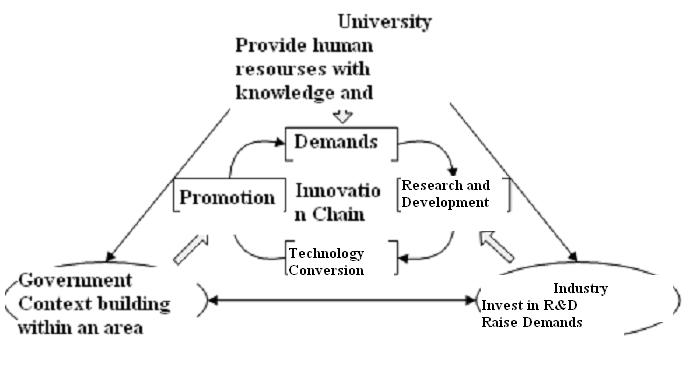
Pic2. University-Industry-Government Innovation
3.The Three Parties and their Influence on the Econet
Through the above analyses, one comes to see that the innovative mechanism of the university-government-corporation econet brought changes to the traditional mode of research and development, linking the three of them to a more widely applicable innovative system. This is different from that in the traditional mode where most innovative activities take place in universities. Therefore, it is necessary to reposition and analyze again the role and functions of the three components in the econet.
3.1 University
In the Econet, universities, as important suppliers of knowledge and technology, directly participate in the production, spread and application of knowledge. They serve as the origin of technological advancement and innovative activities and the training center of the high-flyers in these aspects. Universities are also actively involved in the conception of new ideas, new products and new technology. Through training, education, consultation, product conversion and other methods, they efficiently advance the spreading of knowledge, information and technology, as well as the realization of the market value.
As a result, the roles of universities in the Econet mainly lie in these following four aspects. Firstly, they provide Econet with new knowledge and technology, including basic knowledge as well as applied knowledge and technology. Secondly, they provide Econet with high-quality human resources. Universities turn out graduates, engineers and scientists through education and training, which guarantees human resources in the Econet to improve their own ability to innovate. Thirdly, new enterprises can be derived from universities continually. By producing enterprises of technique steadily, universities convert high-tech achievements, which facilitates the prosper of the Econet. Fourthly, by establishing Science Parks, universities function as incubators of enterprises. University science parks can keep converting the latest science and technological achievements, supplying sophisticated enterprising science and technological achievements, as well as influencing and prompting the development of high-tech industries.
With the spreading of knowledge economy, the "intrinsic logic" of universities' initial mission has been transformed and broadened from knowledge transmission (education) to knowledge creation (scientific research) as well as the business application of new knowledge created (business establishment). In order to achieve such conversion, the universities' independence to determine the strategic direction is required. In addition, universities need to interact with other institutes based on the principle of equality, supplying development strategy and cooperation programs for the development of the economy and society.
3.2 Government
As the main body of the establishment of Econet, the government is the organizer, constructor and maintainer of innovation network. The government mainly plays three roles in the construction of Econet. The first one is director. The government directs the cooperation between universities and enterprises by means of conducting propaganda as well as the economic, legal and policy tools. The second is promoter. By making some policies and regulations, the government can subsidize some scientific research projects with financial support in scientific funds, and give preferential treatment such as tax concessions to independent-innovation projects. The third one is coordinator. The government mainly provides data and measure consultation, designs the blueprint of the cooperation between universities and enterprises, keeps track on the operation situation of universities and enterprises and adjusts its policies in time.
Though the government is not the main body who directly participates in innovation activities, as the sole principal part having the ability to institute regulations, it can create an efficient and long-lasting innovation-incentive environment, correct the defects of market in the innovation of universities and enterprises. As a result, the government acts as a bridge in the activities of innovation system. Specifically, its function mechanism is demonstrated mainly in three aspects. Firstly, macroscopic guidance. Governments of all levels should precisely grasp current trend of the development of economy and technology, carefully make plans for the reconstruction of traditional industries and the development of booming industries, according to which the governments should scientifically seize the cooperation mechanism of universities and enterprises. Secondly, policy guidance. That is, the government should reinforce the guidance in policy. With parameter regulating and main controlling means of finance, the government can promote the combination between universities and enterprises according to their needs. Finally, system guarantee. This includes establishing market mechanism and sound serving system of information, consultation as well as testing, offering agency and legal service and so on.
To conclude, the establishing of Econet is also the process of the government constructing new types of management model. The government should stick to the principle of "small government, big society", absorb management into service, and macro-control the general development of Econet by means of economy, policy -orientation and legal tools.
3.3 Industry
In the Econet, corporations are closely connected to the market, so they understand the needs from the market. Their understanding offers them a clear view on the developing trend of new technology, and spurs them to update their technology. In word, the industry is the center of the Econet standing on the crossroad of producing, disseminating, and applying knowledge, so their innovative motive and capability limit the performance of the whole network.
As the main subject in the network, industry dominates innovation of the Econet in three ways. First, the industry sector determines innovation. Directed by government’s polices on industry and technology, and make a quick and timely decision on the development of new technology in accordance of the demand of the market and their own situation in the market.
Second, the industry sector invests in innovation. The corporations select, implement and finance the projects fit in their development vision on their own, and the risks of investment should also be carried by the businesses.
Third, the industry sector is the subject of R&D, which requires the training and recruiting talents as well as the investment and setting of related facilities to build a complete technology innovation institute. The market-oriented R&D of new technology can be carried out by relying on their internal institutes, or by supporting research institutes or universities on certain projects.
Fourth, the industry sector assumes the risk of innovation and cultivates the benefit of innovation. Once fail, corporation will suffer all the losses of innovation. More risk means more benefits. The industry sector will be rewarded generously on their assumption of responsibility, namely the positive effect of innovation.
As the subject of innovation in the operation of the network, the industry sector should utilize internet resources. Therefore, the industry sector should pay more attention on upgrading the ability of cooperating with external organizations, accepting internet resources, and utilizing internet on innovation.
4.Conclusion
Comparing to traditional university-government-industry relationship, Econet excels in three areas. First, Econet is relatively loose in organization, and their relationship is built on an equal ground of interest. Different from the hierarchical structure in traditional organizations, each member is equal and independent regardless of the scale and competence, joining the network in hope of complementing with each other in strategy, interest and resource through collaboration.
Second, each member of the network mutually benefited from each other. Under the innovation system, the three parties complement each other in resources, so that their strengths can be fully performed while their problems can be solved. As a result, the three parties gained competence both themselves and as a whole.
Third, the mutually benefited relationship produces synergistic effects in the process of R&D and other innovative activities. For example, the Econet can integrate all types of innovative resources and allocate them effectively; it can divide the work and cooperate in a more practical way; the cost of trading can be saved and the risk of innovation can be lowered; the sharing of knowledge and spreading of new technology can be made possible; more talents and projects will join the Econet. All these effects improve the efficiency of the members in innovation, and propel regional technological innovation and industrial upgrading, and finally result in a new Econet with sustainable innovative capability.
Therefore, university-government-industry Econet is an efficient and flexible resource allocation pattern, and presents a new solution to the building of an innovation system. In the system, to establish a healthy and efficient bound among the three parties—university, government, and industry is critical. Also the core value of Econet lies in the diversity of universities, industry and government owns various value systems and functions. The Econet integrates the three parties in developing local society and economy. Since the network connects forces from knowledge sector, administrative sector and industry sector, a more solid foundation is laid for regional development of economy and society while the three parties can join hands in innovation and achieve common progress.
One critical basis of establishing the concerted effort is to break the traditional boundary, including subject, profession, region and concept boundary, and construct new mechanism for management, education and social operation on the cut of the boundary. This requires universities, government and enterprises to convert the traditional roles, establish the concept of equality, cooperation and win-win situation, and give full play to their professional skills to actively participate in the Econet innovation system.
Referrences
[1] Henry Etzkowitz, Three Helix, trans. Zhou Chunyan, Dongfang Publishing House, 2005.
[2] Hu EH, Problems and solutions in niversity and industry cooperation, R&D Management 2002, 14(1):54-57.
[3] Tu J, Wu GS, Three Helix and its application inChina, Science and Research Management 2006(5):75-80.
[4] Iansiti M, Levien R, The Keystone Advantage: What the New Dynamics of Business Ecosystems Mean for Strategy, Innovation, and Sustainability, Commercial Press,Beijing, 2006.
[5] Ge F, Modern Ecology, Science Press,Beijing, 2002.
[6] Iansiti M, Levien R, Strategy as ecology, Harvard Business Review, 2004(4):236-264.
[7] Boston Bank. MIT: The Impact of Innovation [EB/ OL]. (1997). http:// web. mit.edu/ newsoffice/ founders/ TofC. Html.
(The paper was published in the 12th IACEE World Conference on Continuing Engereering Education in October, 2010)
Henry Etzkowitz. Triple Helix. Trans. Zhou Chunyan.Beijing: Dongfang Chubanshe, 2005. pp 243.