——A Case Study ofTsinghuaUniversity
MA Yongbin, WANG Aiyi
(SchoolofContinuing Education,TsinghuaUniversity)
Abstract:In the learning city construction, the traditional higher education institutions are taking reformations toward two directions: those to do with providing lifelong learning opportunities and those to do with cultivating lifelong learners. As a top university located in the culture and education center ofChina,TsinghuaUniversityhas taken on a multi-dimensional role in the process of eliminating regional education unbalance and promoting lifelong learning. This essay will takeTsinghuaUniversityas an example to analyze the roles and responses of higher education institutions in the learning city. Particular emphasis will be placed on the following three aspects: (1) the conceptions and significances of learning city construction; (2) the policy background and the practical models of learning city construction inChina; (3) the challenges and reformations of higher education institutions under the background of learning city construction-a case study ofTsinghuaUniversity. Based on the above discussions, this paper will also demonstrate the implementation and effects of Ma’anshan learning city pilot project initiated byTsinghuaUniversity, which can also be seen as a vivid snapshot of successful cooperation models between universities and cities jointly construct a learning city project.
Keywords:Lifelong Learning, Learning City, Higher Education Institutions
Introduction
In the late sixties of 20 century, the notions of learning society gained considerable currency and was regarded as a new form of social ideality in a number of countries. A learning society is made up of different kinds of learning organizations, such as learning individuals, learning families, learning communities, and learning cities. As for the concept of learning city, different scholars take different views on it. In this essay, the author defines it as a city that addresses individual fulfillment as well as social cohesion through promoting lifelong learning of all the citizens. It was not until 1990s that the concept of learning city had risen up into a widely international movement with the endeavors of the international organizations, such as UNESCO, OECD, and EU. In the process of constructing a learning city, the higher education institutions relying on their excellent faculties, rich learning resources and advanced technologies should make a distinctive contribution. To fulfill this historic mission, the traditional higher education institutions need adopting series reformations and innovations under the guidance of lifelong learning.
2. Learning city: Conceptions and significances
2.1 The meanings and characters of the concept
The concept of learning city has a history extending as far as the late1960s. During this period of time, lifelong learning thoughts were revived by the advocacy of three international organizations (UNESCO, OECD, and EU) and have become a fundamental goal of social and political policies. Lifelong learning has multi-modalities, whether it is called as “lifelong education”, “recurrent education”, “adult education” or ”permanent education” the core idea is all the same, that is providing education opportunities for all the people across their whole life, from the cradle to the grave.
The learning city is closely related with the idea of lifelong learning. It is an operational concept which integrates lifelong learning into the city strategic plan and transforms the lifelong learning ideas into concrete initiatives and action plans. The learning city encompasses varied learning organizations, such as learning families, learning communities, learning villages and learning towns. It is also a necessary part of a learning society which provides suitable environments for varied learning activities and makes lifelong learning into realities.
Thus, the concept of learning city has transcended the geographical scope. It is more than a region with modern architectures, advanced technologies and developed economies. They are communities where lifelong learning has been established as the principle, where varied education providers (formal and informal) are organized in a systemic and comprehensive way and where learning activities can happen at any time in any places.
Although different cities have formed different learning city patterns appropriate to the particular needs of their own localities, learning cities have a number of common characters which make them significantly differ from the traditional cities. As a learning city, it is
ü Regarding lifelong learning as an organizational principle and a strategic city goal;
ü Promoting citizen’s harmonious development (knowledge, skill, attitude, etc.) as well as enhancing the social cohesion and economic development of the city;
ü Providing continuum learning opportunities for all the citizens, from early childhood education to the elder education;
ü Integrating all kinds of learning resources from formal education(K-12) sectors to informal education sectors, into a learning network;
2.2 The significances of the learning city construction
From the sociological perspective, cities are always regarded as the main strengths impelling social reformations and developments Therefore, the construction of the learning city is an important tool to realize lifelong learning conceptions and a breakthrough to establish a learning society. Meanwhile, cities are also the most appropriate forms to carry out lifelong learning activities because of their core status in population, politics, economy, culture and education. Besides, constructing a learning city has other significances. It can be divided into three levels:
Ø Individual level. The learning city will greatly enhance personal fulfillment, cultivate more adaptable, creative individuals through development of a learning culture.
Ø Economic level. The learning city will greatly promote economic development, improve the core economic competitiveness and enhance continuous development of the city.
Ø Social level. The learning city will strengthen social cohesion and civic engagement by providing equal learning opportunities.
Furthermore, there are some special meanings forChinaestablishing learning cities.
Firstly, the learning city construction is an effective way to transformChinafrom a country hindered by a heavy population burden into a country with rich human resources. Now,Chinais at one of the most crucial periods of economic development and social reform. The most obvious problem that would hinder this process is population problem which has already brought up several serious social problems, such as employment issues, environmental destruct and morality loses, etc. They all have direct relationship with the low level of population diathesis. How to effectively deal with these problems and successfully transformChina’s huge population burden into rich productive human resources? The learning city construction has provided us with a very good answer.
Secondly, the learning city construction will accelerate the paces of social and economic development, promoting the establishment of a well-off society inChina. The learning city is a new mode of modern city development, which not only means developing matured lifelong learning systems but also means setting up a series of modern city conceptions and starting up related reformations adapting to the new rising knowledge economy. This process will make the city more efficient and productive and will greatly impulseChinato have a jumping development in socio-economic areas.
Thirdly, the learning city construction will promote the harmonious development ofChina. The fast speed of economic development inChinahas also accompanied with many social conflictions and disharmonic phenomenon, such as unbalanced incoming assignment, deteriorated environments and abnormal development of human beings. It is very crucial forChinato solve these problems for the sake of a further development while learning city construction has proved to be an important approach.
3.The policy background and the practices of learning city construction inChina
3.1 Policy background
Lifelong learning is not a new concept inChina, which can be traced back to an ancient educator named Confucius, who brought forward the lifelong learning idea more than two thousand years ago. But it is not until 1990s when it became a hot topic under the impact of knowledge economy. More and more people have recognized the significance of lifelong learning. Furthermore it is also reflected in some national policies and regulations adopted by the government.
Since the late 1990s, three particular pieces of legislations have been passed concerning lifelong learning. In 1993, the State Council issued “The Outline for Education Reform and Development inChina,” which put forward the concept of lifelong education for the first time. In 1996, “The Education Law of P.R.C.” was adopted by the National People’s Congress, which clearly prescribed thatChinawould accelerate the process of education reform and encourage a variety of education forms to establish a lifelong education system. Shortly after the adoption of the Education Law, the Ministry of Education formulated the Action Scheme for Invigorating Education Towards the 21st Century in 1998, in which the government replaced “lifelong education” with “lifelong learning” and it clearly stated that “China will establish a lifelong learning system in2010”(the Action Scheme for Invigorating Education Towards the 21st Century,1998). It was also regarded as the milestone in promoting a lifelong learning system inChina.
In 2002, lifelong learning has become a necessary part of the national plan. The Sixteenth National Congress of the CPC put forward thatChinawould build up an “All people learning and lifelong learning society” by the year 2020 to enhance people’s all-round development and accelerate the process of building a full welfare society. It also emphasized that China should strengthen continuing education and professional training, construct a lifelong learning system, and provide equal learning opportunities for all the people. (The report of the Sixteenth National Congress of the CPC, 2002)
Although no detailed operational plans were outlined in any of these documents, lifelong learning has transformed into a widely movement acrossChina. Activities of constructing learning cities, learning communities, learning enterprises and learning families are carrying through nationwide.
3.2 Learning city movement
Shanghai is one of the earliest cities inChinato advocate lifelong learning and put it into practices. As early as 1990,Shanghaiinitiated the learning city project and has adopted follow-up measures to encourage lifelong learning. Since then, many cities actively took part in this process. In 2000, Changzhou Municipal Government of Jiangsu Province adopted the “Resolution onConstructingLearningCity.” In the same year, the Beijing Municipal Ministry of Education issued “The Opinions on Promoting Community Education, Building a learning Capital.”
At the end of 2003,Chinaheld the first national lifelong learning conference inBeijing. It was regarded as the turning point of learning city movement. Experts from more than 60 cities, such asShanghai,Dalian,Beijing,Changzhou, got together and jointly issued a “Manifesto ofLearningCityConstruction”. The manifesto pointed out nine concepts, namely humanism, equal learning opportunity, lifelong learning, human resources construction, learning ability, creativity, competition and cooperation, harmonious development, and city civilization. (2003). Since then, the learning city construction has transformed from spontaneity and infantility into the stage of cooperation and maturity.
By the year 2009, there are more than 200 cities in China have definitely set up their goals on constructing a learning city, more than 10 cities have instituted and implemented a series of policies and resolutions to enhance lifelong learning activities, and a number of cities have listed the goal of constructing learning cities into “The Tenth five-year Plan”.
3.3 Learning city models
During the process of constructing learning cities, three patterns of learning cities with distinctive features have emerged. The first is the “Learning for city civilization” model, which means promoting city civilization by means of lifelong learning. The typical example is Beijing Chaoyang District model. The second is the “Learning for city core competivity” model, which means improving the city’s economic competence by encouraging lifelong learning. The typical example isChangzhoupattern. The third is the “Learning for citizens’ harmonious development” model, which means enhancing citizen’s all-round development through lifelong learning. The typical example isShanghaimodel.
The three different models just addresses three fundamental objectives of lifelong learning: personal development, social cohesion and economic growth. The cities will orientate their own objects properly according to their concrete conditions and characteristics. While many cities inChinahave possessed of these three tendencies simultaneously, Ma’anshan City of Anhui province is one of the examples.
BecauseChinahas not set up a matured social education system comparing with western countries, the prominent feature of learning city construction at the present stage is to provide all kinds of available education resources for all the people and enlarge the education chances.
4.The challenges and reformations of higher education under the background of learning city construction
It is customary to divide the work of higher education into three domains: teaching, research and community services. The wide spread of lifelong learning conceptions and activities have greatly challenged the traditional higher education paradigms. The university should foster and support lifelong learning in each of its three functions. It is in this context that the higher education institutions need to reconsider their roles and missions within the domain of lifelong learning. One of the common trend is to move the higher education system in the direction of becoming an open learning system which can be accessed by learners at different times, in different ways and for different purposes at various stages of their lives and careers----a system that promote lifelong learning not merely at the margins for small groups of “mature” people, but in its basic shape and structure.
From our perspective, the higher education institutions can play an important role in the process of learning city construction, because they have possessed of abundant learning resources, advanced technologies and excellent faculties, which are the key factors making up of a learning city. Besides this, the higher education institutions are always the education and cultural centers of the specific communities, which are also the best suitable places to organize lifelong learning activities.
Thus, the higher education should establish a new education paradigm which regard lifelong learning as a basic guideline and carry out series reformations and innovations to fulfill this historical mission. As part of this recognition, universities and other institutions of higher education have had to consider their place within the total domain of lifelong learning. Broadly speaking, these reformations can be divided into two parts: those to do with providing lifelong learning opportunities and those to do with cultivating lifelong learners.
4.1 Providing lifelong learning opportunities
(1)Promoting New Access Policy
Traditionally,the development of higher education institutions in China is a close system which just likes an ivory tower separated from the society and serves for the few elitists who are the winners of the Entrance Examination. At that time, only those who are in the age of 18-25 graduated from high schools and are not married can have the chance to take part in the Entrance Examination. This strict policy has prevented many people who are eager to learn from accessing to excellent learning resources.
The essence of lifelong learning society is ensuring everybody has equal learning opportunities, which call the higher education institutions to take some measures enhancing this process and transforming from elite education to popular education. It is under this background that the Ministry of Education inChinaissued the blue print of “the reformation of Higher Education Entrance Examination” (2001). According to the new accessing policy, everybody whatever his (her) age, marriage status and education background can take part in the Entrance Examination. Thus, promoting new access policy has two objectives: one is giving a chance to adults who missed the opportunity for higher or further education; the other is to make lifelong learning accessible to adults from any socio-economic background. Soon after that, the reform has taken into effect. Many older “non-traditional students” even at their sixties or seventies and those who had not entered or completed upper secondary schools become the candidates for the Entrance Examinations.
(2)Setting up new Academic Program
Currently, the lifelong learners inChinacan be divided into four types. The first is a compensatory type, which refers to those people who have missed the educational chances in their early age and want to make up for it. The second is developing types which refers to those people who have already had sound education background while want to improve their skills, knowledge and seek for a better development through continuing study. The third is a transforming type which usually refers to those people who want to switch to another new field or adapt to the new working environment through educational training. The last type is a leisured type which refers to those people who want to make their life more beautiful, rich and colorful through learning.
There is no doubt that the traditional degree-centered university program could not keep up with this new trend, the higher education institutions need exploring new ways to satisfy these multiple learning demands. Continuing education which characterizes as a flexible academic program has gained recognizance in recent years and emerged from the edge to the center. Along with undergraduate education and graduate education program, continuing education has become a necessary part of the university activities, as important as initial education and research. In the 1995 Education ACT, continuing education was explicitly stated as a legal responsibility for all higher education institutions for the first time. It greatly influences the university strategies. In China, almost all the university have set up the schools of continuing education or the adult education schools, or evening colleges providing multiform learning programs orientated at the above five types of lifelong learners.
(3)Applying ICT in delivering learning resources
In the process of constructing a lifelong learning society, ICT has proved to be an effective carrier to transmit learning resources and enlarge education chances. By using ICT, the university becomes more open and the learning process becomes more flexible, every learner whatever their places can access to the learning resources at any time. Human being’s education activity has been greatly widened and extended.
Distant learning which based on ICT can provide lifelong learning opportunities to a wide range of learners currently excluded from education, such as the students in poverty areas, disabled students, those in employment, etc. Under this circumstance, China Ministry of Education started up the Modern Distance Learning project, which encouraged some qualified universities applying ICT to transfer their education resources. In 1999, China Ministry of Education authorizedTsinghuaUniversityand other three universities as the first set of experimental units. By 2006,Chinahas established a total of 68 universities with web institutes, more than 3,000,000 candidates have enrolled in distant learning. (2006) According to the official statistic, the enrollment of distant learners has constituted about 17% of the total number of the university students throughout the whole country. (Yaoxue Zhang, 2004).This greatly enhances the popularity of higher education and promotes the construction of lifelong learning society inChina.
(4)Increasing new providers in higher education
The traditional universities look conservative and cautiously when taking measures to enlarge the education opportunities and there are still a small group of people have the chance accessing to them. With the increasing demands for higher education, there arise some new forms of higher education providers. With the emergence of new higher education providers, the traditional universities are no longer the monopolies of the knowledge, their hegemonic status are powerfully challenged.
The new higher education providers have provided multiform learning opportunities for the people who are excluded by the traditional universities. The enterprise universities which born out of enterprises have attained a portion of marketing in employee training and adult education training areas; the virtual or open university which based on ICT effectively transmit excellent learning resources to the remote areas; and the community colleges which focus on satisfying varies needs of community residents have gained widely popularity.
4.2 Cultivating lifelong learners
In the framework of lifelong learning, the traditional higher education is no longer an ending point preparing for the individual’s future life, but rather a basic and necessary part of lifelong learning system. It is in this context that universities are under pressure to examine their objects, faculties and teaching methods, as well as their curriculums, in order to ensure that their graduates are armed with appropriate knowledge and attributes that will help them to become independent, lifelong learners.
(1)Regulating teaching objects——the transition from preparing for work to cultivate the attributes of lifelong learners
The traditional higher education object usually focuses on knowledge and skills that prepare the graduates qualifying for their future work. Under the background of lifelong learning, the higher education institutions should regulate and rearrange the levels and grades of the traditional education object. As professor Candy pointed out, the new higher education object system will give much emphasis on lifelong learning. Graph 1 gives us a vivid explanation: In the new object system, cultivating learners with lifelong learning attributes have become the core part instead of the specific knowledge and skills. While in the traditional model, lifelong learning is just a derived object.
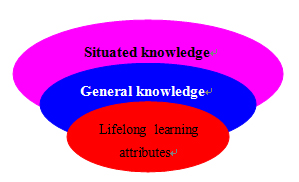
Figure 1. The new levels and grades of object systems in lifelong learning society
In our opinion, lifelong learning attributes including two aspects: one is cognitive factors, such as lifelong learning knowledge and skills; the other aspect is non-cognitive factors, including learners’ attitudes, sensibility and willingness.
(2)Curriculum reformation
The provision of learning opportunities throughout life challenges the traditional curriculums of the university which has privileged the provision of education to students between 18 and 24years. Many researchers have pointed out that a university curriculum promoting lifelong learning should possess the following characters:
Ø Providing systematic introduction to the specific field;
Ø Offering a comparative or contextual framework for viewing the field of study;
Ø Broadening the student knowledge and providing generic skills;
Ø Offering some freedom of choice and flexibility of structure;
Therefore, the traditional curriculum structure design should obey the principle of diversity and flexibility. There are three attempts: one attempt is setting up the modularize courses, which means separating the curriculum content into small, independent and standardized units; the second is setting up core curriculums, which are made up of general discipline or basic curriculums, aims at cultivating learners with the general knowledge and skills which can transfer to other fields; the third is setting up adult orientation curriculums, which adapt to the characters and demands of adult people. As we mentioned above, the prominent challenge the universities are facing in the learning society is the increasing enrollment of adult learners. Then how to reform the current degree curriculum and strengthen the link between basic theories and practical working areas is the most important issue the universities are facing. Many universities have introduced separate courses, part-time courses and evening courses in the regular provision to meet the demands of older, non-traditional students.
(3)New teachers roles and teaching methods
Teachers are the key factors that influence whether the higher education institutions can play important roles and successfully train lifelong learners in the learning society. In our opinion, the teachers in the learning society should transform from the single role of transmitting knowledge, skills and solving problems to play multiform roles. The first is teachers themselves should become lifelong learners. It is not only the requirement of the professional development, but also for the reason of establishing lifelong learning models for the students. The second is teachers should become partners with students. There are several distinctive differences between the new type of teacher-student partnership and the traditional teacher-student relationship. (See Table 1)The third is teachers need changing from experts to mentors and guiders; they are no longer the dictators controlling knowledge and skills.
Table1. Comparisons of two different teacher-student relationship models
Items | Traditional teacher-student relationship model | New type of teacher-student partnership model |
Leadership fashion | Dominance, obedience | Negotiate with each other |
Decision making | Top to bottom | From top to bottom and from bottom to top |
Organizational culture | Authority culture | Democracy, equality and cooperative culture |
Organizational structure | Bureaucracy | Flat |
Relationship with environment | Occlude | Opening |
In addition, the teachers need adopting some new teaching methods that encourage graduates to become lifelong learners. Some scholars have pointed out that these new methods have the following characters: (1) they make use of peer-assisted and self-directed learning; (2) they include experimental and real-world learning; (3) they make use of resource-based and problem-based learning; (4) they encourage the development of reflective practices and critical self-awareness; and (5) as appropriate, they make use of open learning and alternative delivery mechanisms. (Shirley Walters)
5.The responses of higher education institutions in the learning society: A case study ofTsinghuaUniversity
InChina, many colleges and universities are taking measures to promote lifelong learning in the above mentioned areas. As a public university inChina,TsinghuaUniversityis an active advocator and supporter of lifelong learning and has taken on a multi-dimensional role in the process of constructing a learning society inChina. In 2001,TsinghuaUniversitywas authorized a national project on lifelong learning by the MOE inChina. The lifelong learning project assumed by Tsinghua University included four parts: Studies on the theory of lifelong learning system; Construction of the technical platforms for lifelong learning system; Construction and integration of lifelong learning resources; Pilot lifelong learning projects construction. The framework of this research project is shown as following (See Figure 2):
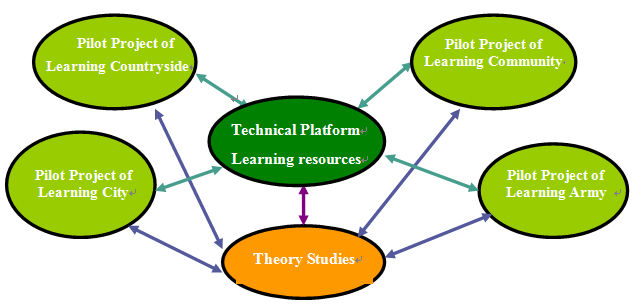
Figure 2. The research framework of the project
With the endeavors ofTsinghuaUniversity, the project has started a series of pilot projects covering four mainstream sections of Chinese society: learning city, learning countryside, learning community and learning army, which makesTsinghuaUniversitya model for colleges and universities to participate in a learning society construction. Here a learning city pilot project, Ma’anshan Learning City Project will be singled out, it is also a typical model of constructing a learning city with the cooperation between universities and cities.
5.1 The general introduction of the learning city project
Located on the bank of the Yangtze River, Ma’anshan is one of the core industrial cities of the Yangtze Delta Economic Zone, one of the most economically prosperous areas ofChina. It consists of 3 districts and 1 county, occupying an area of 1686 square kilometers. The number of its residents has reached 1.2million, 530,000 of which are living in urban areas. Over the past two decades, Ma’anshan has enjoyed a fast, sound and sustainable economic development, major economic achievements such as GDP, fiscal revenue, resident’s income and savings on per capita base, and so on, have been ranked No.1 inAnhuiProvincefor many years. Under the background of a knowledge economy, Ma’anshan city government fully recognized the importance of constructing a learning city. In 2003, Ma’anshan government issued the paper “The Decision on constructing a learning city in Ma’anshan.” In the same year,TsinghuaUniversitychose Ma’anshan as the experimental city to construct a learning city pilot project.
5.2 The objective of the learning city construction
The general objectives of this project is providing lifelong learning opportunities for all the citizens and improving the quality of people as well as enhancing overall competitiveness of the city and urban civilization through learning city construction. The concrete objectives may include two parts: The first part, starting in 2003, taking about 5 years to build the foundational framework of a learning city; the second part, using another five years to consummate the learning city system, cultivate self-directed learning habits of all the citizens.
5.3 The three stages of the project
The First Stage (2003.7-2003.12)—Preparing Stage: Start the project and disseminate the concepts of lifelong learning.
The Second Stage (2004-2007)—Implemental Stage: Construct the foundational framework of Manshan learning city.
The third stage (2008-2012) ---Evaluating and Perfecting Stage: The main tasks will include: to set up a series of high level learning organizations; to establish a lifelong learning system based on school education, adult education, continuing education and community education; to constitute the policy assurance system to provide a suitable learning environment for all the citizens.
5.4 The achievements of Ma’anshanLearningCityProject
Ma’anshan city has achieved a comprehensive and harmonious development since the learning city construction started. It has won several awards, such as “NationalSanitaryCity”, “National Garden City”, and “The most excellent tour city”, “UN Dubai International Award for Best Practices to improve the living environment”, and so on. As for the learning city construction, it has made the following achievements:
First, organized the Directing Council of Ma’anshan Learning City Construction, which is in charge of organizing and implementing the whole project. So far, the council has issued several papers to impel the process, such as “The Decision on constructing Ma’anshan learning city,” etc.
Second, constructed multilevel and multimode platforms for lifelong learning. Based on the Ma’anshan Broadcasting TV University, the project built up the lifelong learning center in Ma’anshan city. The lifelong learning center has four platforms:
n Face to face instruction platform: Including 30 Multi-media classrooms, 3-5 discussion rooms, 1-2 real-time two-way communication rooms, over 800 self study classrooms;
n Learning resources platform: Integrating and developing 500-800 college education course wares suitable for self-directed learning. In June 2004, Ma’anshan successfully introducedTsinghuaUniversity’s resources such as IT, modern public management, enterprise creative ability training, etc. into Ma’anshan city ;
n Technical platforms: Construct a combined network based on Internet, Satellite, Cable TV to transport learning resources; Established supporting service system for learners relying on the Internet;
n Experiment platforms: Built over 20 laboratories to provide basic experiment environment. Opened virtual laboratories through the Internet
Third, enlarged the city library’s capacity and made it open to all the citizens. Set up reading rooms in each community to provide convenient learning environments for the residents. Strengthened the construction of gymnasiums, Science Museums,culture museums, exhibition museums, etc., and took full advantage of them;
Fourth, constructed various city squares, such asHappiness Square,Collaborative Square,Sunshine Square,City Government Square. In the squares, set up newspaper columns, public reading windows, etc., and conducted cultural activities, such as handwriting exhibition, painting exhibition, lecture campaign and reading holiday, etc., to endow the squares with abundant educational functions
Fifth, set up learning bars. By the year 2003, Ma’anshan had set up 40 learning bars in Ma’anshan Broadcasting & TV University. In 2004, it had chosen some rural areas to set up learning bars;
Sixth, set up specific columns in the newspaper and set up educational channels to spread knowledge;
Seventh, focusing on three different kinds of groups, established a specific lifelong learning website, namely: the lifelong learning website for farmers, the lifelong learning website for parents, the lifelong learning website for senior citizens.
Eighth, held a series of academic conferences and training programs. In 2004, Ma’anshan and Tsinghua held the Ma’anshan conference through face-to-face mode and two channel video conference mode. Experts fromTsinghuaUniversitygave speeches on the topic of learning organizations, culture industry and digital learning. So far, Ma’anshan held a series of training programs for government officials, enterprise managers, teachers, farmers as well as unemployed people. There are almost 100,000 people enrolled in lifelong learning activities;
Ninth, constructed learning city assurance system and invigorative system, started setting up evaluation system.
5.5 The role ofTsinghuaUniversityin the project
In the process of constructing Ma'anshan learning city project, Ma'anshan city and Tsinghua University established a comprehensive cooperative relationship, which not only involves the theoretical guidance, the scientific and technological achievements promotion and transformation, training programs cooperation, but also in terms of technology, resources and consulting sectors.
(1) Theoretical mentor and counselor
Lifelong learning and learning organization theory provide the premise and foundations of the learning city construction. The learning city constructors especially the leader groups should understand and master this theory. Ma'anshan city leaders realized that the city was relatively weak in the basic theories and needed introducing outside strength in the theory promotion level. It was because of this reason that the city had taken full advantage ofTsinghuaUniversityin the theoretical guidance and counseling areas of lifelong learning. The function ofTsinghuaUniversitycan be concluded into three parts:
Ø Analyzed and drafted the report on learning needs of Ma'anshan citizens. When the project started, the experts fromTsinghuaUniversityhad come to Ma'anshan city for several times and had taken a compressive and scientific survey on the learning needs and learning conditions of Ma'anshan city.
Ø Put forward the theoretical framework and concrete approaches for learning city construction based on the results of the survey, assisting Ma'anshan city find out the characteristics and the breakthroughs of the project.
Ø Held academic conferences to disseminate and popularized lifelong learning theories and ideas, experts from Tsinghua University had given thorough introductions and explanations on the topic of lifelong learning, e-learning and learning city theories.
(2) Education resources provider
Learning resources is the base of lifelong learning system; it is also the most difficult section of learning city construction. As far as Ma'anshan city is concerned, it has possessed abundant learning resources, such as libraries, museums, exhibitions, primary schools, middle schools and colleges. The prominent problems in Ma'anshan learning resources construction are: the lack of effective mechanisms for integrating current available resources; and the lack of high-quality, high-level educational resources. In this project,TsinghuaUniversityhad transmitted its excellent learning resources to Ma'anshan city via two channels. One is through face to face mode.TsinghuaUniversityhad set up learning centers in Ma'anshan city; many experts fromTsinghuaUniversitywere invited to the learning centers and gave lectures directly to the citizens. The other mode is through ICT,TsinghuaUniversityhad transported more than two hundred of coursewares covering the field of computer, English, management, finance, art and engineering. It also included nearly 100 seminars and lectures presented by Tsinghua experts via Internet Compared with the face to face mode; the distant education model seems more convenient, cheap and effective especially for sharing resources between remote areas and developed areas.
(3) Technical Supporter
ICT application is the typical characteristic of Ma'anshan learning city construction. Then, how to make use of current ICT establishment and provide suitable e-learning environment for Ma'anshan citizens is an important issue in the project.TsinghuaUniversityhas kept the leading possessions in ICT areas, such as Computer Science, Satellite, Cable TV and Digital TV for many years. It is the first university inChinaapplying ICT into distant education. So far, it has set up more than 130 distant learning centers acrossChinasince 1997 and has accumulated valuable experiences in e-learning environment construction. In the technical platform of Ma'anshan learning city construction, Tsinghua University played an important role, from designing the technical framework; solving the technical difficulties, to providing technical guidance and suggestions. With the efforts ofTsinghuaUniversity, Ma'anshan city successfully established a reliable and effective lifelong learning platform based on ICT for the citizens.
6.Conclusion
With the widespread of lifelong learning conceptions, the formal education system is undertaking deep revolution and transforming from modern paradigm to the ecological paradigm which presents a more proactive attitude to the environmental changes. (Paul Clarke, 2004) Under this circumstance, the traditional function and mission of higher education institutions are changing accordingly. As the “China Education White Book” issued in 2000 pointed out, “The higher education must be able to provide learners with lifelong and life wide learning opportunities; to provide them with a series of excellent selected courses and flexible systems for entering and leaving the higher education institutions at any point in their lives. With such efforts, the higher education institutions should promote self-developments and social mobility of individuals and cultivate them becoming citizens actively involved in the civic society. ”
Therefore, the traditional higher education institutions should take “whether it is conducive to cultivate lifelong learners at its maximum”, “whether it is conducive to provide lifelong learning opportunities for all the people throughout their whole life” as the two basic criterions to evaluate the rationality of the teaching process, curriculum setting and teaching service supporting and as the general principle to carry out series reformations and innovations. Through continuous adjustments and adaptations, the higher education institutions are sure to play an important role in the process of constructing a lifelong learning society.
Reference
[1] The Third Session of Eighth National Congress, Education Law of People’s Republic of China, China, 1995.
[2] State Council, Education Promoting Action Towards 21st Century, StateCouncil,China, 1999.
[3] The Sixteenth National Congress of the CPC, the Report of the Sixteenth National Congress of the CPC,China, 2002.
[4] Huang, Wei , “Strengthen the Experiments of Community Education, Promote the Construction of a Learning Society,” China Education Newspaper,Beijing, November, 26, 2002, p.1.
[5] Lian Yuming , LearningSociety,ChinaTimes Economy Publishing House,Beijing, 2003.
[6]ChinaFirst National Learning Conference, the Manifesto of Learning Cities,Beijing, 2003
[7] Paul Clarke,LearningSchooland Learning System, China Light Industry Publishing House, pp38-39,Beijing, 2004.
(The paper was published in 2010 MIT LINC CONFERENCE in May 2010)